View
Project
Project
Webflow
A/B Testing: Guide to Testing and Analyzing Results
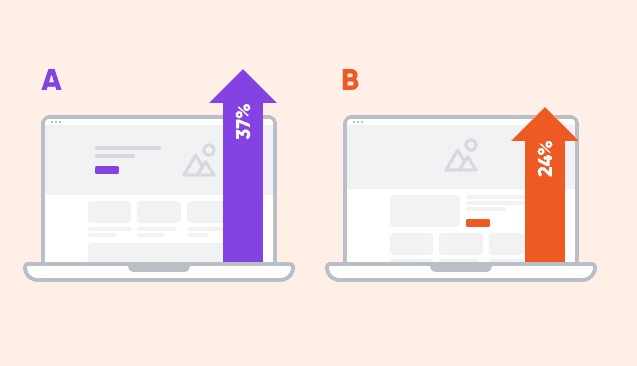
What is A/B Testing?
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a method of comparing two versions of a webpage, email, ad, or any other digital asset to determine which performs better. By presenting two variants (A and B) to different audience segments, businesses can analyze user interactions and make data-driven decisions to optimize conversions and engagement.
Why is A/B Testing Important?
A/B testing helps businesses:
- Improve conversion rates by identifying high-performing variations.
- Enhance user experience through data-driven insights.
- Reduce guesswork in decision-making.
- Optimize marketing strategies for better ROI.
Steps to Conduct a Successful A/B Test
1. Identify a Goal
Define the key performance indicator (KPI) you want to improve, such as:
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Conversion rate
- Bounce rate
- Engagement metrics
2. Choose What to Test
Common elements to test include:
- Headlines and copy
- Call-to-action (CTA) buttons
- Layout and design elements
- Images and videos
- Pricing structures
- Email subject lines
3. Create Variations
Develop two versions:
- Version A (Control): The current version.
- Version B (Variant): A modified version with a single change.
4. Split Your Audience
Randomly assign users into two groups to ensure unbiased results.
- 50% see Version A
- 50% see Version B
5. Run the Test
Implement the test using A/B testing tools such as:
- Google Optimize
- Optimizely
- VWO
- HubSpot A/B Testing
Allow the test to run for a statistically significant duration, ensuring enough data is collected.
6. Analyze the Results
Key metrics to evaluate include:
- Statistical Significance: Ensure results are not due to chance.
- Conversion Rate Differences: Identify which version performed better.
- User Behavior Insights: Understand how users interacted with each version.
7. Implement and Iterate
- Deploy the winning variation.
- Continuously test new hypotheses to refine performance further.
Best Practices for A/B Testing
- Test one variable at a time to isolate its impact.
- Run tests for an adequate sample size to ensure accuracy.
- Avoid testing during unusual traffic spikes that may skew results.
- Document findings to build a knowledge base for future optimizations.